solar thermal systems harness the sun's energy to generate heat, making them ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.

As the demand for sustainable energy continues to grow, many are turning to solar thermal systems as an efficient and eco-friendly solution. While solar photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight into electricity, solar thermal systems harness the sun's energy to generate heat, making them ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
In this blog, we’ll break down what solar thermal systems are, how they work, their advantages, and where they’re best used.
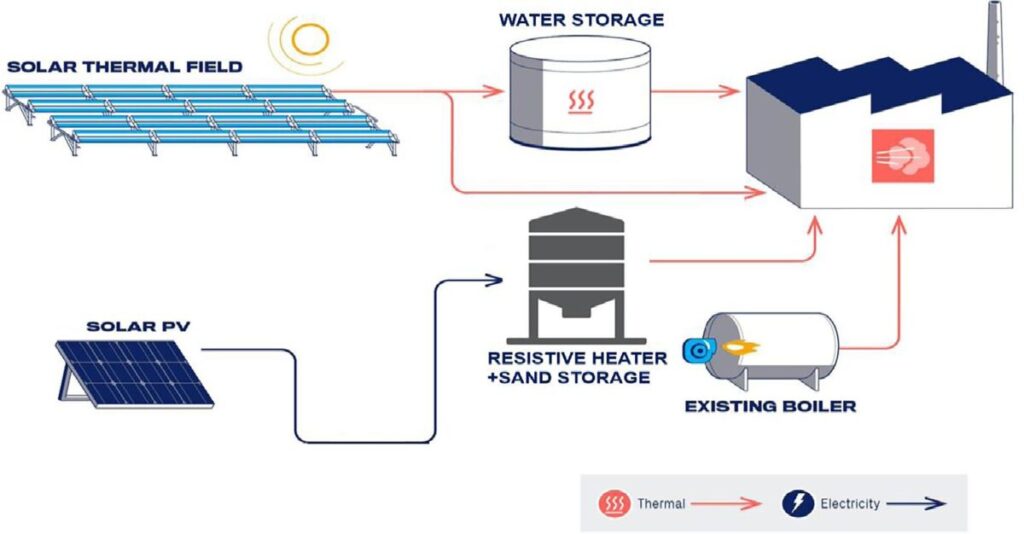
A solar thermal system uses sunlight to heat a fluid — usually water or a heat-transfer liquid — which can then be used for various purposes such as space heating, hot water, or industrial processes.
In simple terms, solar thermal technology captures heat from the sun and puts it to work, reducing the need for electricity or fossil fuels.
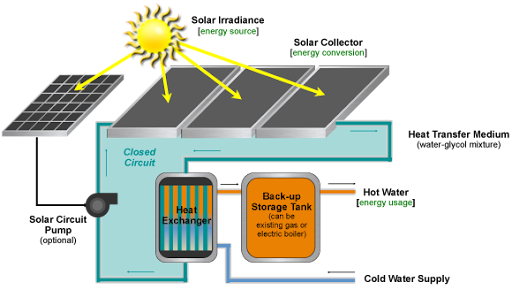
The basic components of a solar thermal system include:
Solar Collectors: These are typically flat-plate collectors or evacuated tube collectors that absorb sunlight and convert it into heat.
Heat Transfer System: A fluid (like water or antifreeze) circulates through the collector and carries the heat to a storage tank or heat exchanger.
Storage Tank: Stores the heated water for later use.
Pump and Control System: Regulates fluid flow and system operation to maintain efficiency.
Depending on the design, systems can be passive (no pumps, relying on gravity and natural circulation) or active (using mechanical pumps and controllers).
Domestic Solar Water Heaters
Most common in homes, used to heat water for daily needs like bathing and washing.
Solar Space Heating Systems
Heat is used to warm indoor spaces, often in combination with radiant floor heating.
Solar Pool Heating
Simple and cost-effective systems to keep pool water warm year-round.
Industrial Solar Thermal Systems
Large-scale systems used in manufacturing processes, food processing, and desalination.
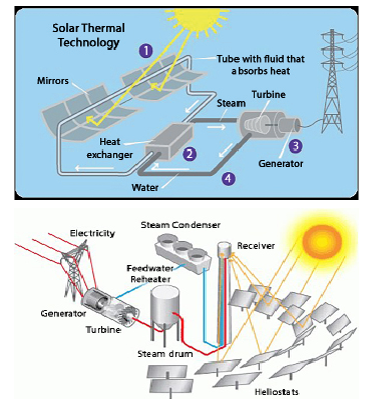
✅ High Efficiency
Solar thermal systems convert up to 70–80% of sunlight into usable heat, much higher than PV systems' electricity conversion efficiency.
✅ Cost Savings
Once installed, they significantly reduce energy bills by cutting down on electricity or gas used for heating.
✅ Environmentally Friendly
They reduce carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
✅ Low Maintenance
With minimal moving parts, solar thermal systems require little maintenance over their long lifespan.
✅ Scalable
They can be used in single homes or scaled up for entire apartment blocks, hospitals, and factories.
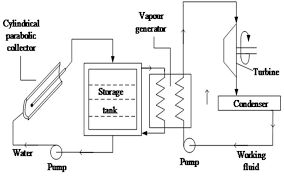
Residential hot water heating
Hotels and resorts
Hospitals and healthcare facilities
Commercial kitchens and laundries
Agricultural drying
Textile and food processing industries
Essentially, anywhere hot water or heat is needed, solar thermal can be a clean, cost-effective alternative.
Initial Investment:
Installation can be costly, though it pays off over time.
Weather Dependent:
Performance drops in cloudy or rainy weather without proper storage or backup systems.
Space Requirement:
Adequate roof or ground space is needed for the collectors.
However, with smart design and proper installation, these challenges can be easily managed.