Solar tracking systems are mechanical structures that move solar panels to follow the sun's position during the day. Unlike fixed-tilt systems, trackers dynamically adjust the panel angle to optimize sunlight exposure. This technology is especially valuable for utility-scale solar farms, but it's also being adopted in commercial and even some residential installations.


Solar panels are a great investment for clean, renewable energy—but what if they could produce even more electricity just by changing their angle with the sun throughout the day? That’s exactly what solar tracking systems do. By following the sun’s path across the sky, tracking systems help panels harvest more sunlight and improve overall energy output.
In this blog, we’ll dive into what solar trackers are, the difference between single-axis and dual-axis systems, and whether they’re right for your solar installation.
Solar tracking systems are mechanical structures that move solar panels to follow the sun's position during the day. Unlike fixed-tilt systems, trackers dynamically adjust the panel angle to optimize sunlight exposure.
This technology is especially valuable for utility-scale solar farms, but it's also being adopted in commercial and even some residential installations.
How it works:
These trackers rotate the panels on a single axis—typically from east to west, following the sun’s daily movement across the sky.
Key Features:
Panels tilt horizontally through the day![]()
Simple design and lower cost than dual-axis
Commonly used in large-scale solar farms
Benefits:
25–35% more energy output than fixed-tilt systems
Lower maintenance than dual-axis
Excellent ROI for high-sunlight regions
Ideal for:
Ground-mounted utility and commercial systems
Sites with uniform terrain
How it works:
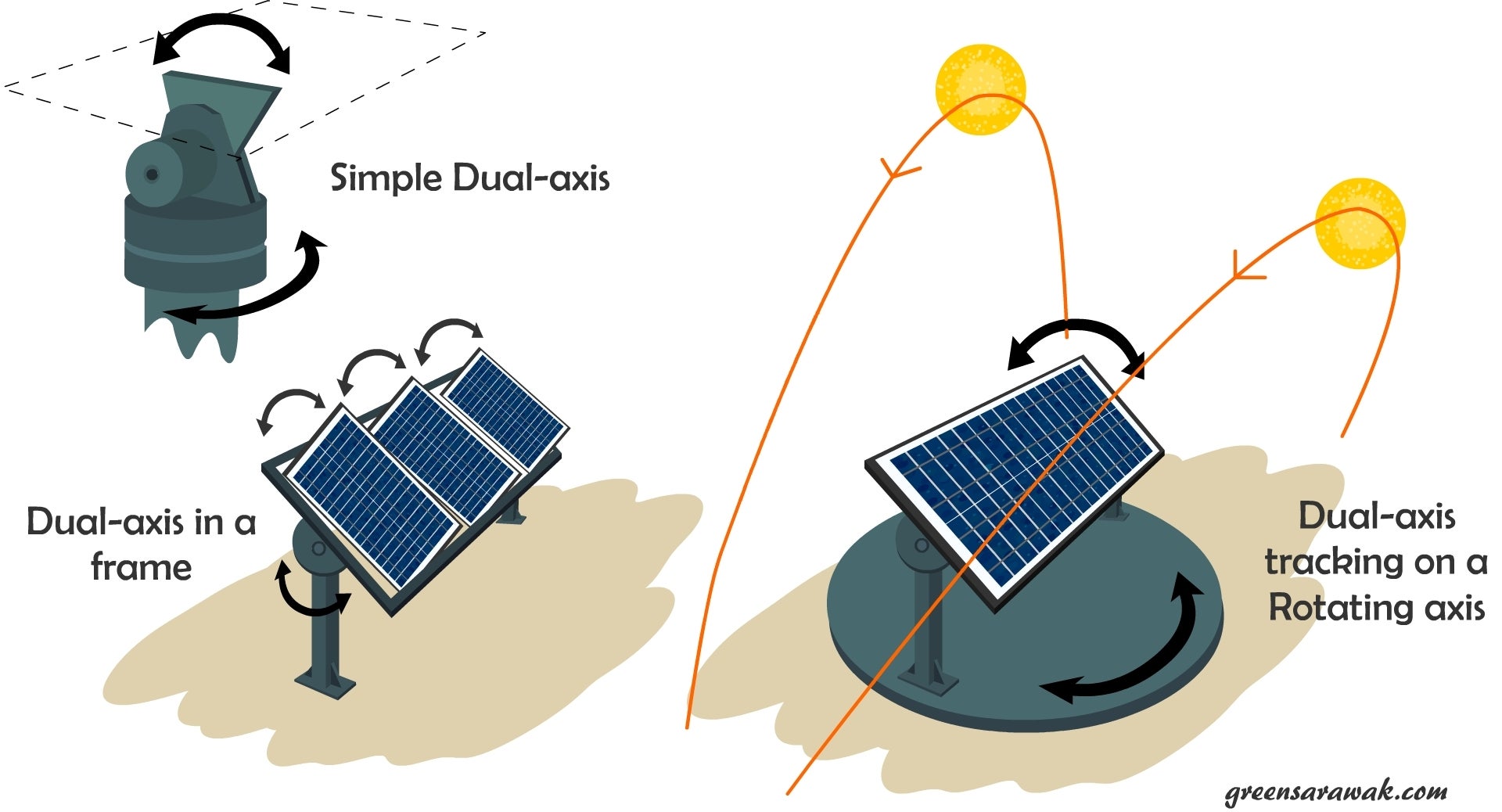
Dual-axis trackers move on two axes—vertical (north-south) and horizontal (east-west). This allows panels to follow the sun’s path throughout the entire year, adjusting for both time of day and seasonal shifts.
Key Features:
Real-time tracking of sun’s position in two dimensions
Maximum sun exposure all day, all year
Higher system complexity and cost
Benefits:
Up to 40–45% more energy compared to fixed systems
Ideal for locations with changing sun angles
Great for areas with limited space but high output needs
Ideal for:
Solar research centers
High-efficiency applications
Compact installations requiring maximum output per panel
| Feature | Single-Axis Tracker | Dual-Axis Tracker |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | East to West | East-West & North-South |
| Efficiency Gain vs. Fixed | ~25–35% | ~40–45% |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Simple | More complex |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Higher |
| Ideal Use Case | Solar farms | Limited space, max output |
✅ More Energy = Better ROI
Trackers significantly boost daily solar output without adding more panels.
✅ Efficient Land Use
Perfect for limited land—maximize energy per square meter.
✅ Smarter Systems
Modern trackers come with weather sensors and automatic stow features (to protect panels during storms).
Initial cost vs. long-term gains
Maintenance requirements
Local weather conditions (wind, snow, dust)
Installation area (flat terrain preferred)
Tracking software and control systems
Solar trackers are not ideal for every situation. In some residential or small-scale cases, fixed-tilt systems may be more practical due to cost and complexity.