As solar technology continues to evolve, one innovation making waves in the energy world is the bifacial solar panel. Unlike traditional solar panels that absorb sunlight from only one side, bifacial panels can capture solar energy from both the front and the back, boosting overall efficiency and energy output.
As solar technology continues to evolve, one innovation making waves in the energy world is the bifacial solar panel. Unlike traditional solar panels that absorb sunlight from only one side, bifacial panels can capture solar energy from both the front and the back, boosting overall efficiency and energy output. In this blog, we’ll explore what bifacial solar panels are, how they work, and the key benefits they offer for residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar projects.
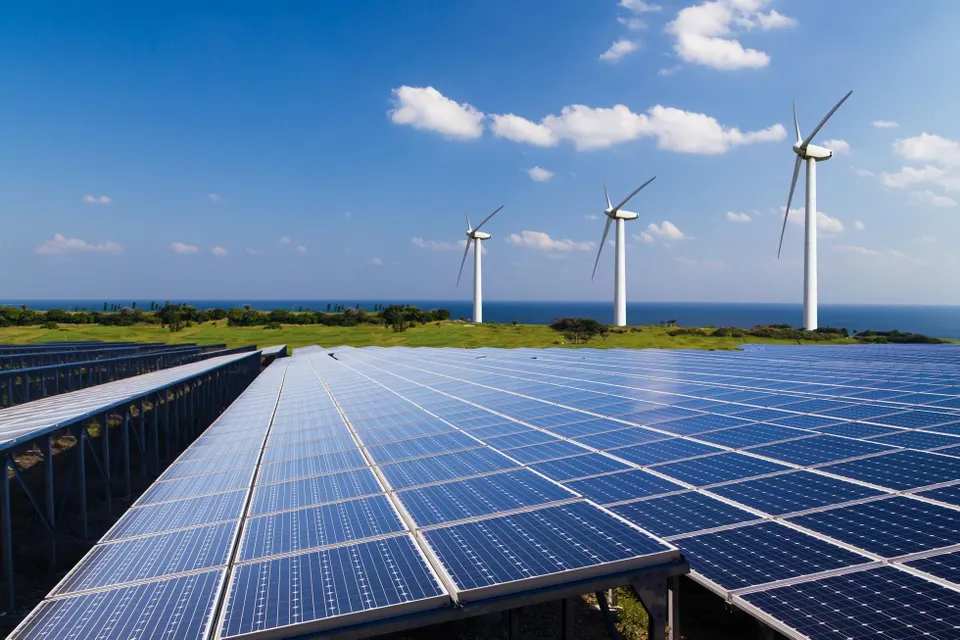

Bifacial solar panels are designed with transparent backsheets or dual glass layers, allowing sunlight to enter from both sides. The front side captures direct sunlight, while the rear side absorbs reflected sunlight from surfaces like rooftops, water, sand, or even snow.
Bifacial panels can generate up to 10–30% more energy than monofacial panels under ideal conditions.
Better performance during cloudy weather and diffuse light conditions.
Most bifacial panels are made with monocrystalline cells, offering higher efficiency and performance consistency.
Despite being slightly more expensive upfront, the higher energy yield reduces the overall cost per unit of electricity over the panel’s lifetime.
Built with double-glass layers, bifacial panels are more resistant to harsh weather, UV degradation, and moisture.
Their sleek, frameless design makes them visually appealing, especially for commercial buildings and architectural installations.
Perfect for open areas, carports, greenhouses, pergolas, and places where sunlight reflects off the ground or surfaces.
However, the long-term ROI of bifacial panels often outweighs these limitations, especially in high-irradiance zones or reflective environments.